Table of contents

Personalization of marketing is becoming a key strategy for companies seeking to optimize their promotional efforts. Using advanced analytics technologies, companies can now precisely tailor their messages to individual consumer needs and preferences. This approach, often advised and used by digital agencies, makes it possible not only to increase customer engagement, but also to optimize marketing resources. How to use personalization to sell more for less while building lasting and valuable relationships with your audience?
Personalization in marketing – what is it?
Personalization in marketing is a strategic approach that consists of tailoring communications, product offers, and shopping experiences to the specific preferences, behaviors, and demographics of individual consumers or groups of consumers The goal is to increase the effectiveness of marketing efforts by creating more relevant and engaging interactions that directly address audience needs and expectations.
Personalization uses advanced data analysis, including information about past purchases, website behavior, reactions to previous campaigns and demographics, to create customized content. Effective personalization in marketing can lead to increased customer satisfaction, higher conversion rates and optimized ROI marketing efforts, as well as building long-term brand loyalty.
Personalization can also be used to improve customer satisfaction, increase conversion rates and optimize ROI marketing efforts.
Benefits of personalized marketing
Personalization in marketing brings a number of benefits to both your company and its audience. What can you gain by investing in personalized and targeted marketing
>
- Consistent shopping experience – personalization shows consumers that you understand their needs, and that makes them more engaged and eager to interact with your brand.
- Improve loyalty, retention and customer lifetime value – customers you treat with personalization show greater loyalty to your brand. What’s more, with personalization, you apply individualized messaging throughout the customer path, making it so that you encourage uch not only to interact, but also to buy and return.
- Increase average conversion rates and average order values – The more relevant your offers are, the more customers will take the action you encourage them to take – be it buying a product, signing up for a subscription, scheduling a consultation, etc. In addition, personalization allows you to win customers with offers based on their previous purchases, interests and real-time behavior, which often leads to an increase in the average value of the shopping cart.
- Maximizing marketing effects – personalization ensures that you always target customers with highly relevant offers. As a result, you don’t waste your time and resources (and your customers’ time and resources). Combined with increased conversion rates and revenue, this makes personalization an extremely powerful tool for maximizing marketing spend and return on investment (ROI). It can even apply to broader branding efforts, such as choosing the best name for a newsletter, article series or YouTube channel to engage a specific niche audience and get higher returns on multimedia content.
Personalized marketing – new trends for 2024
Although personalization in marketing is nothing new, digital marketing is still changing. What personalization trends are dominating in 2024 and will dominate in the coming years?
- Using AI in marketing and personalization – artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing personalization by automating the analysis of large data sets, enabling the creation of more precise and personalized experiences for consumers. AI can predict user preferences, optimize marketing messages and customize offers in real time, increasing campaign effectiveness. Learn more about real-time marketing
- Gamification – incorporating game mechanics into marketing personalization increases user engagement through fun and competition. Gamification can be used to personalize challenges, achievements, or rewards, which motivates users to further interact with the brand and increases loyalty.
- Hyperpersonalization – is an advanced level of customization that uses behavioral, psychographic and contextual data to create uniquely personalized experiences. Brands are relying on an even deeper understanding of individual customer needs to deliver extremely accurate and relatable content.
- Multichannel personalization – ensures consistent efforts across communications channels, from email to social media to mobile apps to physical stores, offering consistent and personalized experiences at every point in the marketing funnel This consistency helps build stronger relationships and better customer service.
- User-generated content (UGC) – allowing consumers to create their own content, which is then used by brands, not only strengthens engagement, but also adds authenticity to brand communications. This content can then be personalized and presented to other users with similar interests.
- Personalized product recommendations – algorithms that analyze previous purchases, products viewed or brand interactions can generate personalized product recommendations. These personalized suggestions increase the likelihood of purchase, improve the shopping experience and increase customer satisfaction.
- Real-time personalization – thanks to technologies such as AI and big data analytics, brands are able to deliver personalized experiences in real time. This means marketing messages can be adjusted on the fly based on users’ current activities and behavior.
See digital marketing trends for 2024 and beyond.
How to successfully implement personalized marketing?
Personalization seems simple only from the customer’s point of view. In practice, as an entrepreneur, if you want to provide personalized experiences to your customers, you need to implement a number of solutions.How to implement personalization in your digital marketing strategy step by step?
1. Ensure data aggregation and unified customer profiles
To even start thinking about personalization in marketing, you must first know:
- who your audience is,
- what products, services, product categories and product features are important to your target audience,
- how audiences interact with your brand, such as what channels they prefer and at what times of the day or week they read your communications.
These data are often in different places with different systems, making it difficult, if not impossible, to get a complete picture about your brand’s audience. To overcome this problem, you need to create a single system for data aggregation. This can be, for example, a CRM system integrated with other tools (such as Google Analytics 4).
2. Perform audience segmentation
Audience segmentation is the process of dividing a large group of customers into smaller subgroups, within which audiences are linked by certain characteristics (e.g., showing interest in a particular product, finding a brand in a particular channel, purchasing a particular product). For audience segmentation, you can use segments in Google Analytics 4 It is a tool that allows you to segment your analytics data, which enables you to deeply analyze the behavior of your audience whether on a mobile app or a website. Segments can be based on parameters such as geolocation, user behavior, traffic sources or demographics. As a result, you can target marketing messages, for example, to audiences who have abandoned a shopping cart in the last 30 days. See more ways to rescue abandoned shopping carts in e-commerce.
3. Develop methods to capture audience data
Ethical customer information acquisition is one of the biggest challenges in personalized marketing. You want to acquire the data, and the user cares about protecting it, so you have to go to great lengths to encourage them to voluntarily provide valuable information. What techniques are worth using for this?
- Registration and subscription forms – a simple but effective tool for collecting basic data, such as name, email address, location, age, etc. Examples include newsletter sign-up forms, where you can additionally inquire about interests or preferences for the information you receive. For example, a clothing store might offer sign-ups for different categories of newsletters, such as news, sales or exclusive collections.
- Online surveys and research – allow to gain more detailed information about users’ preferences, expectations and behavior. A sports equipment company can regularly survey its customers, asking about their preferred types of activities, favorite products or opinions on new collections.
- Social media data analysis – monitoring brand interactions on social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter, allows to understand what content is most engaging for users. Analytics tools, such as Buffer, can help identify popular topics, products or features that generate the most comments and shares.
- Tracking website behavior – using tools such as Google Analytics 4 to monitor which pages are most visited, how long users stay on them, and which conversion paths are most effective. For example, an online store can observe which products are most frequently added to the shopping cart and which are most frequently abandoned.
- Loyalty programs – encourage customers to make regular purchases and at the same time enable the collection of data about their shopping habits. For example, a coffee shop chain may offer a loyalty program that rewards customers for frequent visits, while also recording their favorite products and the time of their visits.
You can still use cookies to obtain information about your audience, as Google has changed its policy in this regard and decided to maintain the current way of cookies. remember, however, that the user must voluntarily consent to the use of cookies.
4. Identify your key performance indicators
To effectively implement personalization in marketing, you need to know where you are at and what fects you want to achieve. Key performacne indicators (KPIs) will be useful for this purpose. How to determine them before implementing personalization?
- Remember that each KPI should be closely linked to the company’s overall business goals. For example, if the main goal is to increase sales, relevant KPIs might include conversion rates, average order value, or purchase frequency.
- Determine exactly what you want to achieve with personalization. Is your goal to increase user engagement, improve retention rates, or perhaps to make your email campaigns more effective? Based on these goals, select the KPIs that best reflect progress in these areas.
- For each of your personalization goals, select specific KPIs For example:
- For increasing engagement: metrics such as time spent on page, number of visits per user, or content interaction rate.
- For improving retention: subscription renewal rate, frequency of returns to the site, or churn (customer loss) rate.
- For email campaigns: email open rate, click-through rate (CTR), and conversions from emails.
- Determine how you will measure each of the selected indicators Determine what tools and technologies will be used to collect data, and how often it will be analyzed. Make sure all data is measured consistently and accurately.
- Regularly analyze results based on defined KPIs and adjust your personalization strategies based on the data obtained Analysis of the results allows you to identify effective practices and elements that need improvement.
5. Select the marketing channels where you will implement personalization
You know the saying that Krakow wasn’t built in an instant? In implementing personalization, you can’t act without a plan either. To avoid burning through your marketing personalization budget, consider first in which channels you want to implement activities to begin with. Don’t kidnap yourself with a hoe in the sun –choose two channels to start with – for example, a newsletter and a website/mobile app.
6. Find ideas for marketing personalization
If you are just beginning the process of personalizing your brand’s marketing, look for ideas for action. You can include the following in thisc elu:
- organize a team brainstorming session,
- do research in your industry and see what marketing personalization solutions your competitors are using,
- organize Six Thinking Hats Sessions – this is a method developed by Edward de Bono in which participants change their “thinking hats” to look at a problem from different perspectives (e.g., emotional, objective, creative). This method can help the team consider different aspects of personalization from multiple sides,
- prepare a team Role Playing meeting – in this technique, team members take on the roles of customers and go through different scenarios of buying or interacting with the brand. This can reveal new opportunities for personalization and improve empathy with the customer.
7. Take care to implement personalization on the website/app
Don’t have an idea for personalization activities on your website or internt app? Take advantage of our inspiration. What you can implement:
- on a service page:
- personalized greetings – use location information or previous user visits to customize a welcome message on the homepage, such as “Welcome back, [name]! We have new offers especially for you”,
- dynamic service suggestions – based on the user’s history of interaction with the site, suggest services that may interest them. For example, if someone has frequently visited the business consulting site, you can suggest articles or webinars on business development.
- Interactive chatbots – integrate chatbots that, based on a user’s previous questions, can provide more personalized answers and service suggestions,
- on the skep internt website:
- product recommendations based on behavior – based on the analysis of the behavior of iz akup display products that may be of interest to the user, such as “Based on your last visit, you may be interested in…”,
- personalized alerts and promotions – users can receive notifications about promotions or the availability of products they have observed or added to their shopping cart but did not purchase.
- adaptive layouts and filters – customize the page layout and available filters according to user preferences, for example, showing the product categories they browse most often in the top positions.
- in the mobile apllication:
- geolocation and personalized offers – using the user’s location, the app can offer region-specific promotions or suggest products available at the nearest stationary store,
- personalized UI/UX – allows users to customize the appearance of the app according to their preferences – they can choose the themes, layouts or features that best suit their needs.
- Calendar integration – service applications can suggest appointments and service reminders based on data from the user’s calendar, such as reminding users of the anniversary of a product purchase and suggesting service.
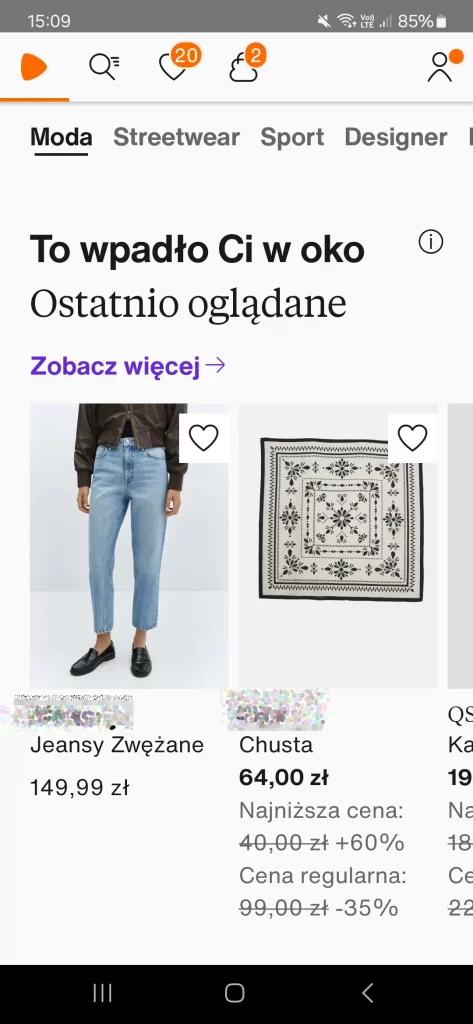
Screen from Zalando mobile app
Summary
Summary, personalization in marketing is a key tool that enables businesses to achieve greater efficiency in their operations while reducing operational costs. By leveraging advanced analytics and user behavior data, marketers can tailor their messages and offers to the individual needs and preferences of each customer. Such a strategy not only increases customer engagement and loyalty, but also improves the ROI of marketing efforts. However, personalization requires constant customization and testing, which means companies must be prepared to continuously invest in technology development and data analysis.
Was the article helpful?
Rate our article, it means a lot to us!
Let's talk!
CEO and managing partner at Up&More. He is responsible for the development of the agency and coordinates the work of the SEM/SEO and paid social departments. He oversees the introduction of new products and advertising tools in the company and the automation of processes.